Navigating Mortgage Qualification, Comparison, & Insurance for Homebuyers:
1: Understanding Mortgage Qualification:
Navigating Mortgage Qualification, Comparison, & Insurance for Homebuyers is the first step towards homeownership, requiring a clear understanding of several key financial criteria. Lenders typically assess your credit score, income, debt-to-income ratio, and employment history. A high credit score indicates good financial management and increases your chances of securing a favorable mortgage rate. Lenders look for a stable income that can cover mortgage payments, typically requiring documentation such as tax returns, pay stubs, and bank statements.

Navigating Mortgage Qualification, Comparison, & Insurance for Homebuyers addition to income and credit score, lenders consider your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, which compares your monthly debt payments to your monthly gross income. A lower DTI ratio suggests that you have a manageable level of debt relative to your income, making you a lower risk to lenders. Employment history is also scrutinized, as a steady job indicates income stability. Together, these factors help lenders determine your mortgage qualification and the terms of the loan you can receive.
2: Comparing Mortgage Options:
With various mortgage options available, comparing them is essential to find the best fit for your financial situation. Fixed-rate mortgages offer a stable interest rate and predictable monthly payments over the life of the loan, making them ideal for long-term homeowners. In contrast, adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) start with lower interest rates that adjust periodically based on market conditions, which can be advantageous if you plan to sell or refinance before the rate increases.
When comparing mortgage options, also consider government-backed loans, such as FHA and VA loans. FHA loans, insured by the Federal Housing Administration, are popular among first-time homebuyers due to their lower down payment requirements and flexible credit standards. VA loans, guaranteed by the Department of Veterans Affairs, offer competitive rates and no down payment for eligible veterans and active-duty service members. Each mortgage type has unique advantages and potential drawbacks, making it crucial to compare them based on your long-term financial goals.
3: Importance of Mortgage Insurance:
Mortgage insurance plays a critical role in the homebuying process, especially for those with lower down payments. Private mortgage insurance (PMI) is typically required for conventional loans with less than 20% down payment, protecting the lender in case of borrower default. PMI adds to the monthly mortgage cost but allows buyers to purchase a home sooner without waiting to save a large down payment.

For government-backed loans, different types of mortgage insurance apply. FHA loans require mortgage insurance premiums (MIP), both upfront and annually, which help to fund the program and protect lenders. VA loans, on the other hand, do not require mortgage insurance but have a funding fee that helps cover the costs of the loan program. Understanding the different types of mortgage insurance and their costs is essential for budgeting and making informed homebuying decisions.
4:Tips for Navigating the Homebuying Process:
Navigating the homebuying process can be complex, but several strategies can simplify it. First, get pre-approved for a mortgage to understand how much you can afford and to demonstrate your seriousness to sellers. Pre-approval involves a preliminary evaluation of your financial status and can streamline the home search process. Next, work with a real estate agent who understands your needs and the local market, providing valuable insights and assistance in finding the right home.
Additionally, conducting thorough research and understanding all associated costs is crucial. Beyond the mortgage payment, consider property taxes, homeowner’s insurance, maintenance costs, and potential homeowner association fees. These factors impact your overall budget and long-term financial planning. Finally, don’t rush the decision. Take the time to visit multiple properties, compare prices, and ensure that the home you choose aligns with your financial and personal goals. Proper planning and careful consideration can lead to a successful and satisfying home purchase.
5: Understanding Mortgage Qualification:
Qualifying for a mortgage is a critical step in the homebuying process, requiring an understanding of various financial criteria. Lenders evaluate your credit score, income, debt-to-income ratio, and employment history to determine your eligibility for a loan. A high credit score indicates responsible financial behavior and can secure a better mortgage rate. Stable and sufficient income, supported by documentation such as pay stubs and tax returns, is also crucial, as it assures lenders of your ability to make regular payments.
Another vital aspect of mortgage qualification is the debt-to-income (DTI) ratio. This ratio compares your monthly debt obligations to your gross monthly income, helping lenders assess your financial health. A lower DTI ratio suggests you have a manageable debt load, increasing your attractiveness as a borrower. Employment history is also reviewed, with a steady job history indicating income reliability. Understanding these factors and how they interplay can help you prepare effectively for the mortgage application process.
6:Comparing Mortgage Options:
With numerous mortgage options available, making the right choice requires careful comparison. Fixed-rate mortgages offer predictable monthly payments and interest rates, making them a popular choice for long-term homeowners. These loans provide stability and are straightforward, with no surprises in monthly payments. On the other hand, adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) start with lower interest rates that adjust over time based on market conditions. This option can be beneficial if you plan to move or refinance before the rate changes.

Government-backed loans, such as FHA and VA loans, also provide unique advantages. FHA loans, insured by the Federal Housing Administration, cater to first-time buyers with lower down payment requirements and more lenient credit criteria. VA loans, guaranteed by the Department of Veterans Affairs, offer competitive rates and no down payment for eligible veterans and active-duty service members. Each mortgage type has distinct benefits and potential downsides, making it essential to compare them based on your specific financial situation and long-term goals.
7: Importance of Mortgage Insurance:
Mortgage insurance is crucial for buyers who cannot make a substantial down payment. Private mortgage insurance (PMI) is typically required for conventional loans with less than 20% down, protecting lenders if the borrower defaults. PMI adds to the overall cost of the mortgage but enables buyers to purchase homes without waiting to save a large down payment, facilitating earlier homeownership.
Navigating Mortgage Qualification, Comparison, & Insurance for Homebuyers government-backed loans, different mortgage insurance structures apply. FHA loans require mortgage insurance premiums (MIP), including an upfront fee and annual payments, which safeguard lenders and support the loan program. In contrast, VA loans do not require mortgage insurance but have a funding fee that helps cover the program’s costs. Understanding these insurance types and their associated costs is vital for accurate budgeting and making informed homebuying decisions.
8:Tips for Navigating the Homebuying Process:
Navigating the homebuying process can be daunting, but several strategies can help simplify it. Start by getting pre-approved for a mortgage to understand your borrowing capacity and demonstrate your seriousness to sellers. Pre-approval involves an initial evaluation of your financial status, streamlining the home search process. Additionally, working with a knowledgeable real estate agent can provide valuable market insights and assistance in finding a suitable home.
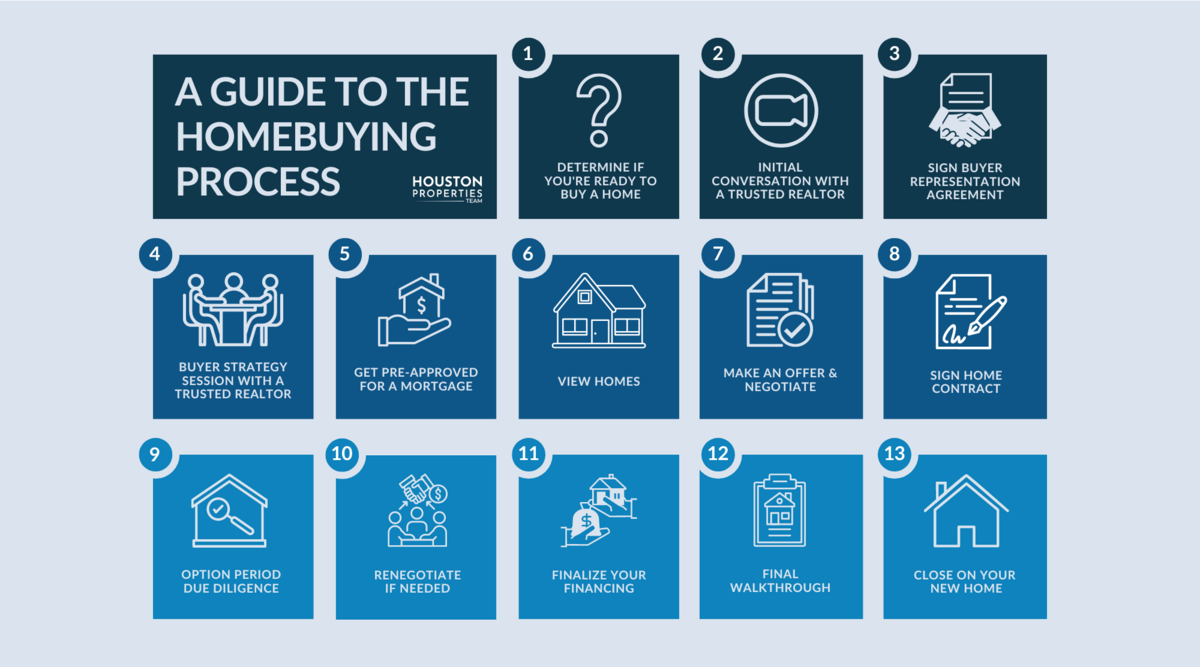
Thorough research and understanding all associated costs are also critical. Beyond the mortgage payment, consider expenses like property taxes, homeowner’s insurance, maintenance costs, and potential homeowner association fees. These factors affect your overall budget and long-term financial planning. Lastly, take your time making decisions. Visit multiple properties, compare prices, and ensure the chosen home aligns with your financial and personal goals. Proper planning and careful consideration can lead to a successful and satisfying home purchase.
